
 Time:2024-02-27
Time:2024-02-27
 Author: evvo
Author: evvo
 Read: 929times
Read: 929times
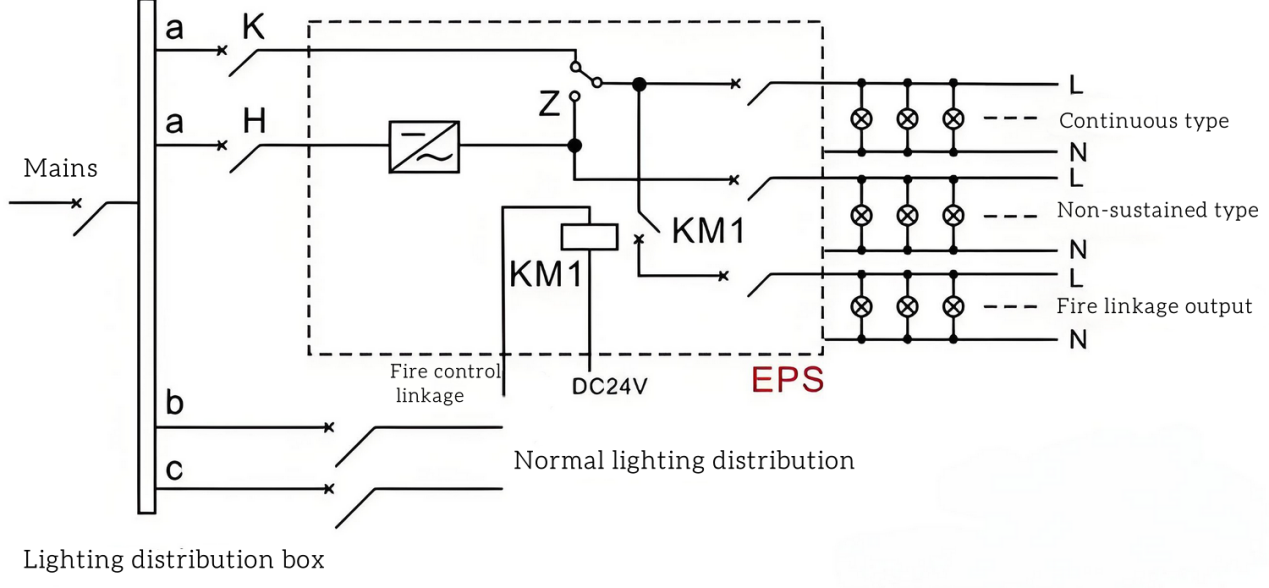
1. Both EPS power supply and UPS power supply can provide dual power output options. UPS power supply To ensure the quality of power supply, the inverter is preferred. In order to save energy, EPS power supply gives priority to mains power supply. The two power supplies differ significantly in the design standards of the rectifier/charger and inverter to suit their respective application needs.
2. The UPS power supply adopts the online working mode, once the failure occurs, the system can send an alarm in time, and use the mains power as a backup to ensure that users can quickly identify and solve the fault, so as to avoid greater losses caused by accidents. In contrast, EPS power supplies use offline mode, as the final power supply guarantee, its reliability requirements are extremely high, can not simply be regarded as a backup UPS. If the EPS power supply cannot provide emergency power through the battery in the event of a mains failure, its function will be useless, which may lead to serious consequences.
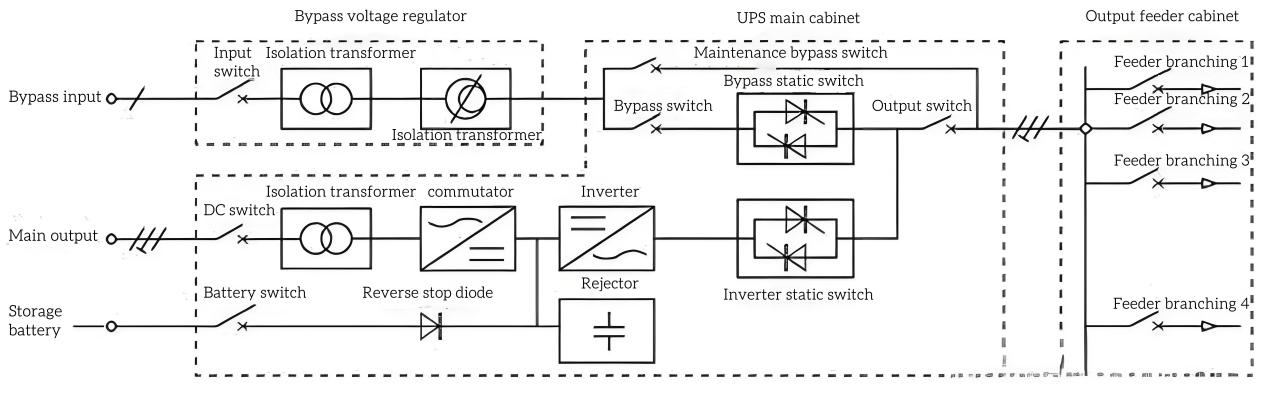
3. UPS power supply mainly provides power for computers and network equipment, because the load characteristics of these devices (that is, the input power factor) are relatively consistent, the state stipulates that its output power factor should reach 0.8. In contrast, EPS power supplies serve the field of power security and fire safety, and their load characteristics are more complex, including inductive, capacitive and rectified nonlinear loads. Therefore, the output power factor of EPS cannot be simply set to 0.8, which will be specified in the national standard. In addition, part of the load is started after the mains interruption, which requires the EPS to provide a large starting current. At the same time, EPS power supplies need to have better dynamic response and stronger overload capability. Based on these different needs, EPS and UPS power supplies have different distribution in terms of technical design indicators.